‘Ten Crucial Days’, from Dec. 25th 1776 to Jan. 3rd 1777’
Prelude to the Battle:
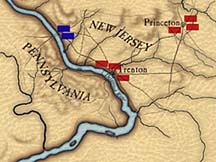 Many Americans don’t realize that George Washington & his troops crossed and re-crossed the Delaware River a total of four times in the waning days of 1776. The first time was in early December when he left New Jersey in retreat from the British.
Many Americans don’t realize that George Washington & his troops crossed and re-crossed the Delaware River a total of four times in the waning days of 1776. The first time was in early December when he left New Jersey in retreat from the British.
The second was when he crossed back into New Jersey to attack Trenton (Dec.25-26). After Trenton was taken, Washington thought it wise to put the river between his army and the more powerful British army, and so back they went back to Pennsylvania. When Washington arrived back at the Pennsylvania camp, he received word that Brigadier General Cadwalader had not crossed the river on Christmas due to the bad weather and mistakenly assumed that Washington would not have crossed either.
Upon learning that Washington had not only crossed but had beaten the Hessians, the shame-faced Cadwalader finally crossed and entered the unoccupied Trenton. Washington did not want to put a negative spin on the so far victorious venture by ordering Cadwalader to retreat, and so crossed the river once again and joined the two commands together on the 29th of December. By this time British General Cornwallis had arrived at Princeton, New Jersey with 8,000 troops. Washington knew he could expect an attack by Cornwallis very shortly and was determined to make a fight of it. Instead of fortifying Trenton, though he put his lines just south of the town on the south bank of the Assunpink Creek.
On Dec. 27th General Cadwalader, who had been unable to land on the Jersey shore on the 26th due to the ice on that shore, reported he was crossing near Burlington, reinforced by militia which was turning up encouraged by the victory. Cadwalader was unaware that Washington had re-crossed the river. He moved into the now empty Burlington and then to Bordentown, reporting that the citizens were hastily removing the red rags nailed to their doors as symbols of loyalty to the crown. He entreated Washington to join him in advancing on the British who were in a panic.
Washington’s troops were at the moment in no condition to advance, further, he was short of food. Moreover, many of his New England troop’s enlistments were due to expire on the 1st of Jan. By the 30th he had improved his supply situation and re-crossed the river. On the 30th he made an impassioned plea to a regiment whose enlistments were about to expire. No one stepped forth to stay. Once again Washington spoke “My brave fellows, you have done all I asked you to do and more than could reasonably be expected. But your country is at stake, your wives, your houses, and all that you hold dear. You have worn yourselves out with fatigues and hardships, but we know not how to spare you. If you will consent to stay only one month longer, you will render that service to the cause of liberty and to your country which you probably never can do under any other circumstances. The present is emphatically the crisis which is to decide our destiny.”
Again the drums rolled, calling for men to step forward, and finally about half the men step out to reenlist. Other officers speak to other regiments with the same success. With the other troops on hand, it will have to be enough. If Washington could maintain the initiative, he might save the Revolution. If he loses a battle at this critical time, it was thought the revolution would collapse.
The Battle of Princeton
 British General Howe orders General Lord Cornwallis to Princeton to gather all available troops for a counter attack. On January 2nd, Cornwallis marches on Trenton with about 6000 men, leaving three regiments of the 4th Brigade at Princeton as rear-guard, under Colonel Charles Mawhood. At Maidenhead (now Lawrenceville) on Jan 2nd, the British meet with American units who begin a fighting withdrawal, ambushing and delaying the British. It is 4 PM when the British finally get to Trenton, to find Washington entrenched but out-numbered and outclassed. Washington has but 5,200 men, many unreliable militia. Washington has deployed his troops on the south side of Assunpink Creek, a strong position, and repels several attempts of the British to take the bridge. Night eventually fell. Since his troops are tired, Cornwallis decided to wait to attack until the morning, when he can “bag the fox” as he called it. His officers want to attack now, fearful of Washington’s known ability to retreat and escape but Cornwallis remained arrogantly steadfast believing that a mere rabble of farmers could never defeat British regulars.
British General Howe orders General Lord Cornwallis to Princeton to gather all available troops for a counter attack. On January 2nd, Cornwallis marches on Trenton with about 6000 men, leaving three regiments of the 4th Brigade at Princeton as rear-guard, under Colonel Charles Mawhood. At Maidenhead (now Lawrenceville) on Jan 2nd, the British meet with American units who begin a fighting withdrawal, ambushing and delaying the British. It is 4 PM when the British finally get to Trenton, to find Washington entrenched but out-numbered and outclassed. Washington has but 5,200 men, many unreliable militia. Washington has deployed his troops on the south side of Assunpink Creek, a strong position, and repels several attempts of the British to take the bridge. Night eventually fell. Since his troops are tired, Cornwallis decided to wait to attack until the morning, when he can “bag the fox” as he called it. His officers want to attack now, fearful of Washington’s known ability to retreat and escape but Cornwallis remained arrogantly steadfast believing that a mere rabble of farmers could never defeat British regulars.
During the night, Washington leaves a hand-full of his men to keep the campfires burning, make entrenchment noises, and keep up appearances, while the rest of the army sneaks around the British forces toward Princeton, where they can attack the rear of the British forces and maybe even capture the 70,000 pound sterling war treasury of General William Howe in New Brunswick. Washington orders his troops to silence and all orders are given in whispers. Taking back roads, the Americans move to the south around the British and swing towards Princeton. Main roads at this time are poor tracks-some of these back roads are little more than trails which had already become unused as the area was settled but the troops stagger along them in the dark all night. Luckily a freeze has set in with nightfall and the roads are frozen and unpassable for both men and cannon.
At dawn, Lt. Colonel Charles Mawhood has begun to follow in the wake of Cornwallis to Trenton, with his 17th Foot of the  4th Brigade followed by the 55th, and the 40th regiment ordered to remain in Princeton. Now the Americans under General Hugh Mercer who had been sent to guard the left flank and the 17th under Mawhood discover each other at the same time, and move to attack. The 55th moves back into Princeton. Mercer and Mawhood each believe they have encountered a patrol. Mawhood has about 276 men, and Mercer 120 with 200 following. Both race to the high ground (now called Mercer heights). Mercer is surprised to run into Mawhood’s men deployed in line. Captain Willie Leslie of the 17th, and nephew of General Alexander Leslie, is killed in the first fire.
4th Brigade followed by the 55th, and the 40th regiment ordered to remain in Princeton. Now the Americans under General Hugh Mercer who had been sent to guard the left flank and the 17th under Mawhood discover each other at the same time, and move to attack. The 55th moves back into Princeton. Mercer and Mawhood each believe they have encountered a patrol. Mawhood has about 276 men, and Mercer 120 with 200 following. Both race to the high ground (now called Mercer heights). Mercer is surprised to run into Mawhood’s men deployed in line. Captain Willie Leslie of the 17th, and nephew of General Alexander Leslie, is killed in the first fire.
After exchanging fires, Mawhood’s regiment charges with the bayonet. Only 20 or so of Mercer’s men have muskets and bayonets, most being slow reloading riflemen whose guns cannot use bayonets. Mercer is mortally wounded and his troops fall back, but Cadwalader’s 600 men of the Pennsylvania militia arrive. They fire and then start to fall back, even though they greatly outnumber the 17th. (Mawhood and the 17th regiment put up a terrific defense, still remembered and honored in Great Britain.)
Washington and his officers rally them, and more troops arrive and Washington himself leads them towards the British. Washington is only 30 yards from the British lines when he orders his men to fire. Both sides do fire, and Washington disappears in the smoke. When the smoke clears Washington is unharmed but Mawhood’s regulars have broken. Washington orders a charge. The British troops retreat, some scattering into the woods, others turning for Cornwallis or New Brunswick. Washington also leads the pursuit, calling “It’s a fine fox hunt, boys!”
In Princeton, the 40th and 55th regiments prepared to make a defense of the town. General Sullivan had his wing of the army moving to sweep into town from the other end, and the British sent out a platoon to outflank them. Sullivan in turn sent out 2 regiments to counter this flanking maneuver, forcing the British back. Now Sullivan’s men met an equal number of British deployed behind a dike in the area of Frog hollow. Sullivan had his cannon brought up, which sent shot into the dike and drove the British into the area of Nassau hall, the main college building at the time.
 The British took shelter in and around Nassau Hall in Princeton. The Americans brought up a cannon, and took two shots at the building. The first bounced off, but the second entered the main room where the troops were holding, and allegedly decapitated a picture of King George the 2nd on the wall! The British in Nassau Hall surrendered.
The British took shelter in and around Nassau Hall in Princeton. The Americans brought up a cannon, and took two shots at the building. The first bounced off, but the second entered the main room where the troops were holding, and allegedly decapitated a picture of King George the 2nd on the wall! The British in Nassau Hall surrendered.
When the British Dragoons make a stand to defend the fleeing troops, Washington called off all pursuit. Washington knew that Cornwallis could move on his rear soon, and he had to keep the army together. Placing a militia unit to destroy the bridge over the Stony Brook, and gathering what supplies could be quickly loaded, he ordered his troops to march to Kingston. Here, it was decided that even though New Brunswick and the British treasury were only a few miles away, and lightly guarded, the exhausted troops could do no more for now. The American Army moved north along the Millstone River to Somerset Court House, now Millstone, where he had to rest his troops.
Back at Trenton on the 3rd, Cornwallis found that the Americans were gone by dawn and at first it was believed they had marched to Bordentown, but soon he received reports of fighting at Princeton and he marched toward Princeton. When his vanguard reached the Stony Brook they realized that bridge over the creek is broken up~ obviously destroyed by the Americans. The militia makes a short stand, forcing the British to stop and form for battle. Washington and the troops are able to get away, and Cornwallis rests his troops for a few hours.
At Kingston, Cornwallis heads for Brunswick and arrives at 6 AM where he deploys troops to defend the town. Washington is a few miles away at Somerset Court House (now Millstone), but his troops are exhausted, some have hardly eaten, and Cornwallis position was not known, except that he was close. Any attack is not considered possible.
On the 4th, after deciding not to attack New Brunswick, Washington continued north, and later that day they arrived in Pluckemin. Protected now by the Watchung Mountains to his east, and with Morristown units behind him, Washington was now safe. He would soon move the army into winter quarters at Morristown.
After The Battle:
The British, who lost 86 killed and wounded at Princeton and two hundred captured, were now ordered by Howe to abandon NJ, except for a line from Perth Amboy to New Brunswick. George Washington, who had about 40 killed and wounded at Princeton, had now driven the British from most of New Jersey, in what is called the ‘Ten Crucial Days’, from Dec. 25th 1776 to Jan. 3rd 1777.
More importantly, the Revolution now had a chance, morale was improved, and Americans once again believed they could stand and face the enemy troops. The British outrages in the invasion of New Jersey had turned many previously on the fence to the side of the revolution against the British. Paper money was acceptable once more and the rebel government and army found support again. General George Washington had learned to fight not the main British army, but its outposts which forced the British to give up any effort to control the environs of America. The French government, encouraged by the British defeats, released supplies to the American war effort. In England, the royal government started losing support for the war. The Crisis was past, even if severe hardship and fighting were yet ahead, in a long and bitter struggle for freedom and independence.
The Treaty of Paris was signed in Paris by representatives of King George III of Great Britain and representatives of the United States of America on September 3, 1783, thus ending the American Revolutionary War and recognizing the original 13 colonies (Delaware, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Georgia, Connecticut, Massachusetts Bay, Maryland, South Carolina, New Hampshire, Virginia, New York, North Carolina, and Rhode Island ) as a new and sovereign nation. GOD BLESS AMERICA! ~ JGT











